
In the past 10 years, open-source software, SaaS, and subscription business models have arisen from David to Goliath status in the workplace. Companies can create flexible, customizable IT ecosystems at a fraction of the initial investment of time and money previously required. This has enabled comprehensive views into productivity and customer analytics. It has brought the easy UX people now expect in consumer products to the work environment.
However, these fast, easy, and cheap solutions have also transformed the experience of work, not always for the better. First, they create a fragmented, even siloed work experience, with gaps that require extensive manual effort to close. Second, and conversely, they engender much duplicate work in overlapping systems, often work that goes unseen, as employees simply put in the time and effort to do it. With both gap-filling and duplicative work, employees are solving the same problems over and over in Sisyphean loops. It may even feel productive but is simply sapping scarce mental resources from their true tasks.
Finally, these solutions are driving an unquestioned push towards automation, which results in dramatic wins for some and losses for many, by both dumbing down and eliminating roles. This may seem like a great way to save money, but it can also demoralize workforces and significantly undermine customer experience.

Marymoore will explore these issues using two workplace software experiences from diverse industries where she has observed striking parallels: mental healthcare navigators for an online employee service and construction information managers controlling massive projects from design to build.
SaaS is here to stay, and there is no easy answer to these challenges. However, Marymoore will recommend a couple of approaches that can help companies, employees, and customers flourish rather than flounder in the sea of APIs.
Images are licensed under Creative Commons License.
The Silicon Prairie Center Innovation Model was developed with a vision to help entrepreneur founders to “Stay Lean, Stay in Control” through a unique entrepreneur live and work incubator model which includes residences, office space, and innovation space all in one location. The Silicon Prairie Center consists of four buildings based in a downtown area with the conveniences of downtown living and working but at a small fraction of traditional tech hub locations allowing the founders to stay lean, minimize burn and subsequently retain more ownership and control of their companies. The Silicon Prairie Center aims to encourage collaboration amongst community members and leverages local cost effective vendors.

Founder Kirk Zeller has a vision that it may be possible to encourage more creative thinking in medical device development through having a film project also based at the Silicon Prairie Center. In May 2020 the romantic comedy, #MyCorona, was filmed at the Silicon Prairie Center and was the first feature film in history to be directed entirely remotely. Characters in the film were inspired by Silicon Prairie Center start-ups and one of the start-up’s products was featured in the movie. The Silicon Prairie Center’s in house creative team is involved in both the film and the start-ups resulting in creative cross-pollination.
Kirk Zeller will share his vision for the Silicon Prairie Center and discuss how he weaves healthcare entrepreneurship, filmmaking, and US-Japan collaborations together at the Silicon Prairie Center. He will provide an overview of each of the start-ups, market access firms, and film projects based at the Silicon Prairie Center.
Dr. Richard Dasher, Director of the US-Asia Technology Management Center and Adjunct Faculty at Stanford University
Images are licensed under Creative Commons License.

Recent events have revealed considerable insecurities in existing business approaches and also pointed the way toward future innovations. For example, the Covid-19 pandemic accelerated the transition of remote meetings and work-from-home employment patterns from their old role of being nice ways to save money to a new role as essential capabilities for ensuring business continuity. Similarly, US – China technology friction has led to greater diversification of supply chains with redundancy in multiple countries in addition to China.

This presentation will examine the relationships between two major engines of business growth, namely globalization and innovation, and (a) big changes that have been widely anticipated, especially the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and (b) sudden changes that were unexpected, e.g. the Covid pandemic. In so doing, it leads to an interactive discussion of capabilities that will allow technology intensive companies to thrive in a more uncertain world.
Dr. Richard Dasher, Director of the US-Asia Technology Management Center and Adjunct Faculty at Stanford University
Images are licensed under Creative Commons License.

Clinical data has been included Electronic Health Records for the past decade or more. Machine learning can be used to analyze this data and predict outcomes for patients based on their characteristics. Use cases will be presented based on research and the development of a platform that can deliver this information to the treating physician at the point of care.
Images are licensed under Creative Commons License.
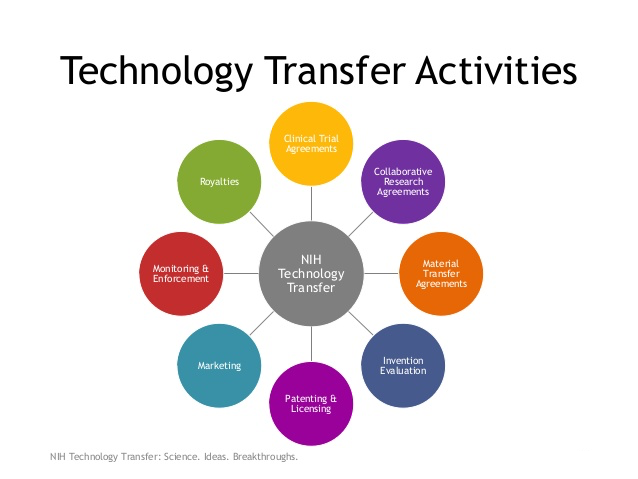
The United States currently leads the world in government support for non-military research and development (R&D), especially support for work that directly relates to health and human development. A focal point for such investments to date in biomedical research has been the National Institutes of Health (NIH), receiving approximately $41.7 billion in fiscal year 2020. Approximately 9% of this funding is spent annually on internal R&D projects (intramural research) utilizing the work of about 9,000 scientists. The other funding is largely utilized to support the work of 35,000 non-government investigators (extramural research) at various colleges and universities in the U.S. and abroad as well as corporate research undertaken at small businesses.
Whether internal or externally based, the biomedical research performed has led to a large variety of novel basic and clinical research discoveries – all of which generally require commercial partners in order to develop them into products for hospital, physician or patient use. Thus, the NIH needs and actively seeks partners and licensees to help develop and commercialize its research into products to help fulfill its mission as a healthcare agency.
The presentation will examine how the NIH technology transfer program works to meet these goals as well as offering suggestions and practical advice for organizations seeking new product ideas or looking to interact with NIH scientists in order to start or expand their businesses. With over 700 products from these license agreements currently on the market, licensing, collaboration, funding or contract activities with NIH cannot be overlooked as part of growth strategies for biomedical firms.
Images are licensed under Creative Commons License.

Machine Learning (ML) in conjunction with synthetic biology allows for efficient biological engineering using the same approach as Google’s use of ML to optimize search, and Autodesk’s to design buildings. Real world examples will be used to illustrate how we use statistical and synbio tools to build better genes, proteins, vectors, and cell lines to cure COVID, make better cheese, and break down toxic chemicals.
Images are licensed under Creative Commons License.

This presentation provides an overview of how the coming wave of Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality, Machine Learning and Biosensing Technology are converging, and elaborates how this convergence will impact clinical care, disability solutions, and personal health and wellness.
Although entertainment, social connection, and gaming is driving the initial adoption of VR and AR technology, the deepest and most significant impact of the next generation of VR/AR technology will be to enhance clinical care and to improve personal health and wellness. VR and AR technology will also help facilitate the shift of medicine from clinic-based care to telemedicine based care, and to facilitate personalized medicine.
We know from decades of clinical research that VR/AR technology can provide breakthrough solutions that address the most difficult problems in healthcare – ranging from mood disorders such as Anxiety and Depression to PTSD, Addictions, Autism, Cognitive Aging, Stroke Recovery, and Physical Rehabilitation, to name just a few.
VR and AR Systems can be used to improve medical training such as surgical skill training and procedure planning by applying simulation-based learning principals. Personal health and wellness will be improved by using VR to promote healthy lifestyles and to reduce stress and anxiety.
VR/AR technology, when combined with Machine Learning and Biosensing technology can be used to improve clinical measurements and assessments by making them more objective and functional. As the cost of healthcare rises, this confluence of emerging technology will be used as the foundation for next-generation telemedicine platforms to reduce costs of care delivery, improve clinical efficiency, and reach previously underserved populations.
Images are licensed under Creative Commons License.
The Triple Ring PIX team is pleased to be an attendee at the 69th annual X-ray virtual conference.
http://www.dxcicdd.com/index.htm